
RDM gives you the advantages of direct access to disks while keeping some advantages of a virtual disk in the VMFS file system.īefore input/output operations, a VM via header file initiates the opening of the RDM volume. The RDM files contain metadata used to manage and redirect disk accesses to the physical device. After that, all read and write operations are sent directly to the RDM volume, without a mapping file. Basically, when you are opening your RDM volume to write data, the VMFS file system grants access to an RDM file on the physical device to realize the options of file locking and access control. In that separate case, virtual disk header files in the VM configuration are viewed as VMFS volume files in the working directory of a VM. You can access the RDM option through a symbolic link referencing RDM in a VMFS volume. Furthermore, RDM-disks also comes in handy when using Microsoft Clustering Services (MSCS), even for both “virtual to virtual” and “physical to virtual” clusters.
#VMWARE ESXI 6.7 TURN OFF STORAGE VMOTION SOFTWARE#
If the storage area network (SAN) uses snapshot software as a backup solution for VMs, you’ll need a direct connection. RDM enables a disk subsystem (storage LUN) of storage devices such as Fibre Channel and iSCSI to be connected to a VM. Raw device mapping (RDM) option is also supported by the VMFS file system. Don’t forget that the rest of the datastore space, including the reserved space designated for disk expansion, is available to all VMs. Nevertheless, this is really an ambiguous advantage since if you configure it in a wrong way, that may result in the “disappearance” of all reserved space, which is leading to the problem with resource distribution between the VMs.
#VMWARE ESXI 6.7 TURN OFF STORAGE VMOTION FULL#
Naturally, it does have an advantage, for it does not reserve space in full by default. As you can figure out, it also isn’t a good fit for the VMs that have high-performance standards. Of course, it means that writing new data for the first time will take longer than anticipated with this disk format. Provisioning more space, just like in the case with Lazy Zeroed, would require, in turn, zeroing out the space you want to use to write new data. Further, upon necessity, it can expand into the required size of provisioned space.

Thin Provision, upon creating a virtual disk, reserves space designated for a disk equals zero namely, it is 0B. Creating and connection of such a disk need a lot more time than Lazy Zeroed disk, and it strongly depends on the speed and size of disk space, but this disk gives away higher performance rates as compensation. Thanks to this, when your VM is writing data for the very first time, there is no delaying in speed required for “zeroing”. Eager Zeroed also creates a new disk in a default format with the space designated for the files is reserved in full, but, unlike the previous configuration, it “zeroes out” the allocated space in advance. Thick Provision Eager Zeroed is a similar thing, only working vice versa both in terms of speed and performance. Efficiency-wise, this type of provision is definitely not the best choice for a VM with high-performance requirements, but, on the other hand, you can create and connect this disk in mere seconds. However, when you overwrite already written data (ergo, use that allocated space for a second time), the old data isn’t “zeroed out” anymore. The old files aren’t cleared and formatted with zeros until the VM writes new data for the first time, and only within the specifically allocated space required for the new data. All the space designated for the files is reserved in full, but it has a few more aspects necessary to mention. Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed is essentially a format for a virtual machine disk that creates a new disk in a default format. Let us quickly remember the key differences. Physical structure of different virtual machine disk formats from VMware In other cases, like with RDM, it’s a header file for a physical disk, albeit it works almost the same exact way as in the previous case. The OS inside the VM is connecting with the virtual disk using specific device drivers.
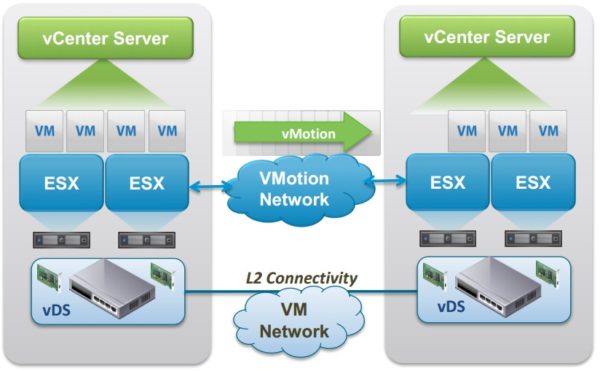
Primarily, a virtual disk for a VM from VMware is basically the same thing as in other hypervisors – a datastore file. Therefore, although I was talking about this topic a while ago here and there, it’s time to get to the point. My beginner colleagues are often wondering what virtual disk is preferable to choose. As the name of this article is hinting, I’m going to discuss the answers to the said questions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
